Whitepaper
Technical design documents and architecture details for the Dstack TEE platform.
dstack Whitepaper
Call for Next Generation Zero Trust Platform
The Web3 ecosystem represents a paradigm shift in digital trust models, fundamentally transforming the relationship between users and application developers. Unlike traditional systems, Web3 empowers users with unprecedented control over their data through the principle of “Code is Law” — once deployed, code operates autonomously beyond external control. This transformation demands robust execution platforms that maintain confidentiality and integrity without relying on centralized trust authorities.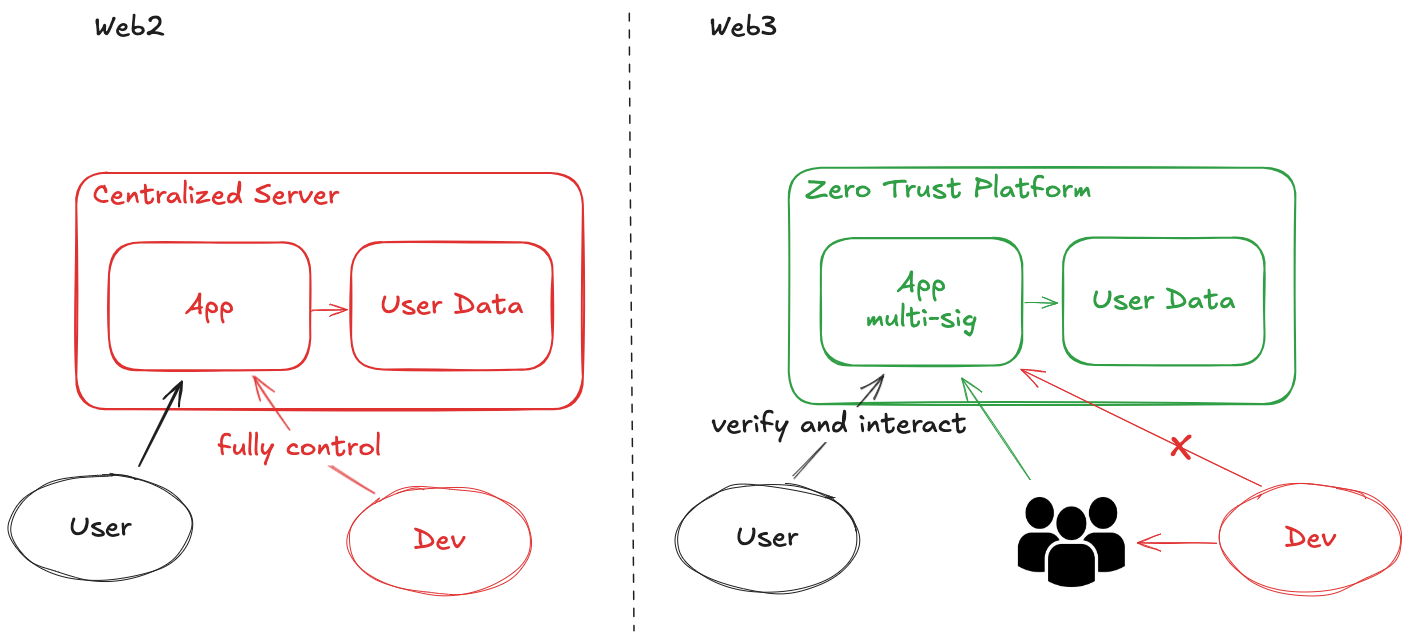
The evolution of trust models from Web2 to Web3, highlighting the shift from centralized control to decentralized governance and execution.
In Web2 systems, developers maintain complete control through proprietary applications and centralized servers, retaining administrative privileges to access and modify user data at will. Web3’s smart contracts, however, represent the first significant advancement toward true trustlessness by executing programs on decentralized platforms (blockchains). Once deployed, administrators cannot affect program execution, and lifecycle management (e.g., code updates) follows coded agreements through democratic governance mechanisms like multi-signature wallets and Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs). This evolving trust model extends beyond basic applications to mission-critical scenarios such as AI model training, where data providers and model developers often have competing interests, and autonomous AI agents designed to operate independently of human intervention. In these contexts, Zero Trust platforms become essential to host applications and enforce verification mechanisms that appropriately constrain developer authority. A Zero Trust platform must enforce the following key principles:
- Code is Law: This manifests in two dimensions: (1) the application logic, once deployed, cannot be changed unexpectedly; and (2) the lifecycle management of code — including deployment, upgrades, and deletion — follows predefined governance rules.
- Censorship Resistance: User data remains beyond the control of any single entity, with data
availability protected against Denial-of-Service attacks. - Full Chain-of-Trust: When users interact with applications on a Zero Trust platform, they
must be able to verify all aspects of that application, including network setup, application identity and code logic, underlying hardware, and execution environment. - Assume Breach: The platform operates under the assumption that compromises will occur,
implementing mechanisms for damage containment, rapid recovery, and minimization of data
exposure during security incidents.
From TEE to Zero Trust Platform
Confidential Computing, particularly through Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs), has emerged as a promising foundation for extending blockchain capabilities to support complex computational tasks with confidentiality guarantees. Recent advances in VM-level TEE solutions, including Intel TDX and AMD SEV, have demonstrated substantial performance improvements and developer-friendly interfaces, making them compelling candidates for Web3 deployment. The integration of GPUs within TEEs now enables verifiable execution of both Large Language Models and AI agents, providing cryptographic guarantees of computational integrity. However, there exists a significant gap between raw TEE technology and the requirements of a true Zero Trust platform. Current TEE implementations face several critical limitations when applied to Web3 contexts:- Security Reliability: Recent vulnerability discoveries in TEE systems have raised significant concerns about their effectiveness as trust anchors. The persistence of side-channel attacks and micro-architectural vulnerabilities undermines confidence in TEE security guarantees, particularly for high-value Web3 applications where a single compromise could lead to catastrophic data exposure.
- Censorship Vulnerability: Conventional TEE encryption schemas bind encryption keys to specific hardware instances, creating single points of failure that contradict Web3’s requirement
for censorship resistance. This architectural limitation means that data availability cannot be
guaranteed if specific hardware instances are compromised or become unavailable. - Vendor Dependencies: Current trust models heavily rely on centralized hardware manufacturers and verification processes, introducing risks of vendor lock-in and potential censorship vectors. This centralization contradicts Web3’s core principles of decentralization and trustlessness, creating systemic risks for the ecosystem.
- Incomplete Verifiability: While TEEs provide Remote Attestation capabilities to verify application and hardware identity, they fail to deliver the comprehensive chain of trust required in Zero Trust environments. Users need guarantees that programs process their data as expected and cannot be modified without proper authorization — capabilities beyond current attestation mechanisms.
a comprehensive framework for confidential containers that introduces three key innovations:
- Portable Confidential Container: Our architecture enables seamless migration of confidential workloads across different TEE instances and hardware vendors, significantly reducing vendor lock-in risks while maintaining robust security guarantees. This innovation directly addresses the censorship vulnerability and vendor dependency limitations by providing hardware abstraction and state continuity across heterogeneous TEE environments.
- Decentralized Code Management: We implement a comprehensive governance framework
that leverages smart contracts for transparent and decentralized management of TEE applications. This system ensures verifiable deployment and upgrade processes, enforcing the “Code is Law” principle by binding application lifecycles to on-chain governance decisions. This innovation addresses the incomplete verifiability limitation by creating an immutable audit trail of application changes. - Verifiable Domain Management: Our novel approach to certificate management ensures that
confidential containers can exclusively control domains and provide native HTTPS support to
TEE applications without relying on centralized authorities. This system serves as a middleware between TEE applications and existing TLS-based networks, enabling users to establish end-to-end encrypted channels to TEE applications without modifications to client software.
dstack Components
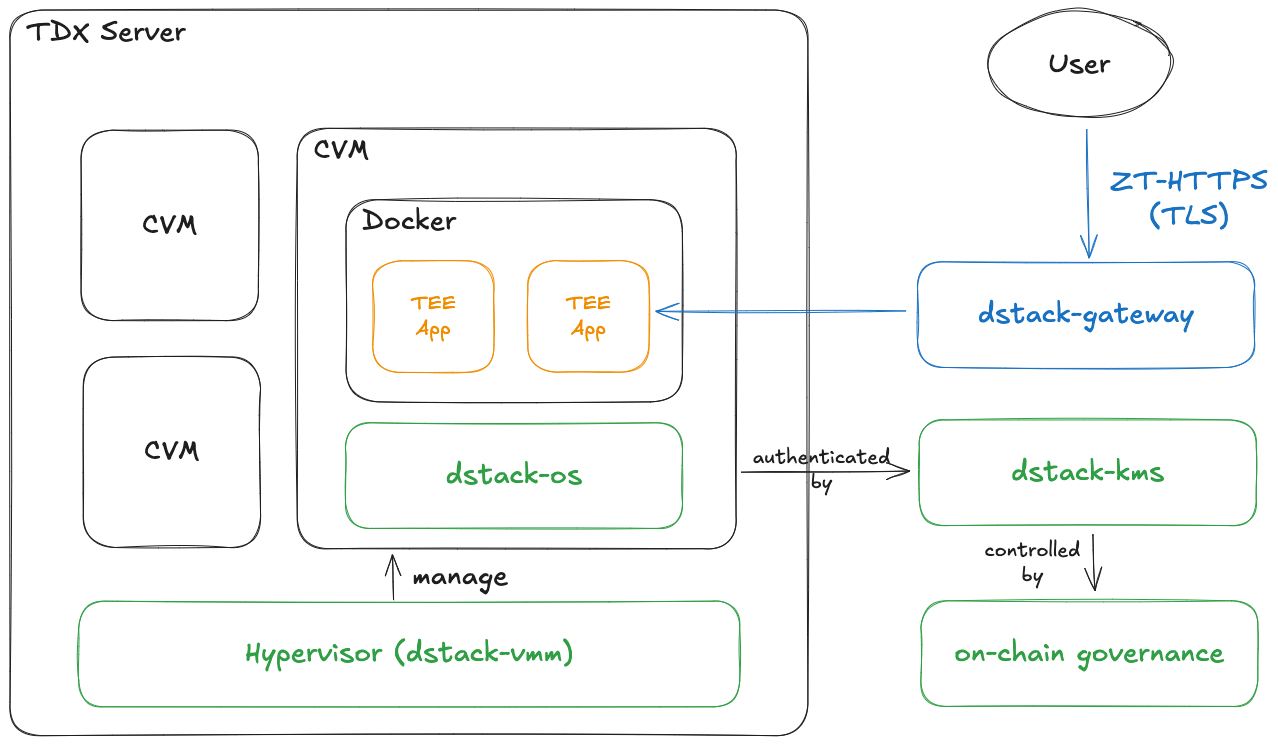
The architecture of dstack, including dstack-os, dstack-kms and dstack-gateway.
- dstack-os: A hardware abstraction layer with a minimized operating system image that eliminates differences in underlying TEE hardware while reducing the attack surface. This component provides a consistent, secure runtime environment across diverse TEE implementations.
- dstack-kms: A blockchain-controlled key management service that replaces hardware-based encryption schemas with an independent service for generating and managing secret keys. This component enables secure data migration across TEE instances and supports key rotation to provide forward and backward data secrecy, mitigating the impact of potential TEE compromises.
- dstack-ingress and dstack-gateway: Complementary systems providing TEE-controlled domain management through different approaches — dstack-ingress enables applications to specify custom domains with minimal integration requirements, while dstack-gateway offers pre-registered wildcard domains requiring no application code changes.
that maintains the performance advantages of VM-level TEE solutions while addressing their inherent limitations in Web3 contexts.
System Design
Portable Confidential Container
Containerization has revolutionized cloud-native application deployment by providing unparalleled portability and scalability through effective data separation. These capabilities are particularly critical for Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) applications, as they directly address the inherent limitations above:- Security Reliability: Containerized applications can be seamlessly migrated from compromised TEE hardware to secure instances, preserving code integrity. Combined with our secure data migration mechanism that ensures both forward and backward secrecy, this approach significantly mitigates privacy leakage risks even when individual TEE instances are compromised.
- Censorship Resistance: The architecture’s inherent scalability provides robust defense against Denial-of-Service attacks. Additionally, by decoupling data storage from execution environments, established data availability solutions can be readily integrated to ensure persistent access to application data.
- Vendor Independence: Our hardware abstraction layer enables confidential containers to
operate across diverse TEE hardware platforms without modification, eliminating vendor lock-in while facilitating rapid adoption of emerging TEE technologies as they become available.
- First, existing TEE implementations generate data sealing keys derived from hardware-bound root keys unique to each TEE instance. This architectural design creates an inherent barrier to portability — data encrypted by one TEE instance cannot be decrypted by any other, even when running identical application code. Prior research has largely circumvented this limitation by restricting TEEs to stateless applications, but this approach severely constrains their utility in complex real-world scenarios.
- Second, TEE implementations from different vendors impose disparate specifications for deployable programs. This fragmentation forces developers to create and maintain multiple artifacts across platforms, each requiring separate (and expensive) code reviews to verify functional equivalence — a process that undermines the trust guarantees central to Web3 applications.
dstack-kms: Blockchain-Controlled Secret Derivation
dstack-kms is a secret derivation service that fundamentally transforms how encryption keys are managed in confidential computing environments. Its primary function is to generate a unique and stable secret (the Root Key) for each application based on its code and configurations. This Root Key serves as the foundation for deriving additional application-specific secrets used for data encryption and verifiable random number generation. Unlike hardware-based encryption approaches, dstack-kms deliberately decouples key generation from specific TEE hardware instances. This architectural decision enables the critical capability of encrypted data migration between different TEE instances, with decryption possible after proper authorization. This feature is essential for achieving true censorship resistance. Given its position as the root-of-trust for the entire system, the verifiability and availability ofdstack-kms are paramount. Unlike previous approaches that assume TEE infallibility, our threat
model explicitly acknowledges that TEEs can be compromised. To address this reality, dstack-kms implements comprehensive key rotation capabilities that provide both backward and forward secrecy for application data. This ensures that even if a specific TEE hardware instance is compromised, applications can be migrated with minimal data exposure.
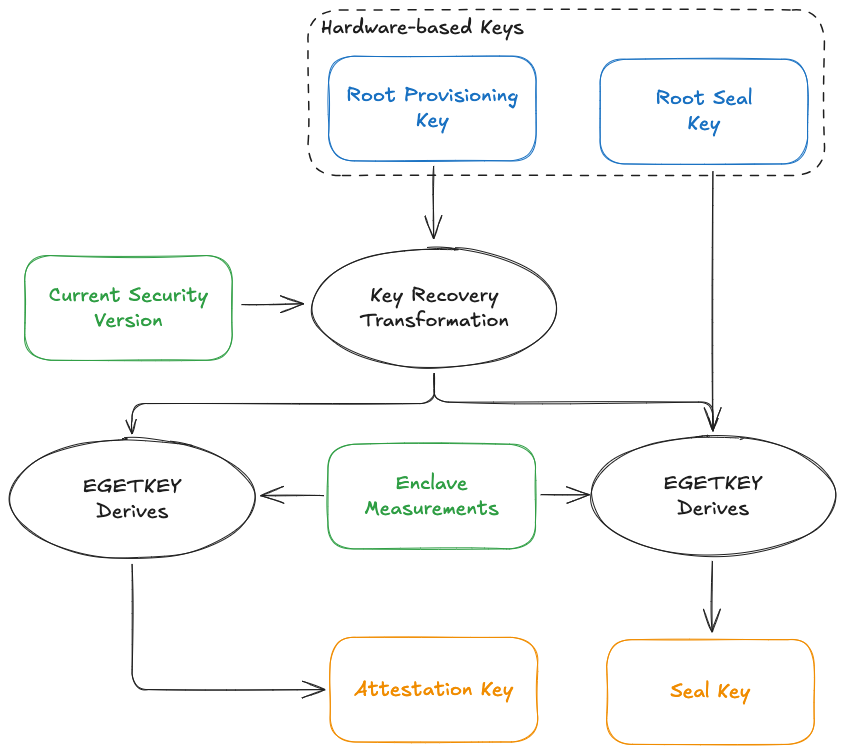
The key derivation hierarchy of Intel SGX illustrates how conventional TEE implementations bind encryption keys to hardware.
- The root key cannot be updated, meaning a compromised TEE with a leaked root key remains
permanently vulnerable even after patching the underlying vulnerability. - Encrypted data becomes intrinsically bound to specific TEE hardware instances, creating single points of failure that contradict Web3’s censorship resistance requirements.
service that ensures encrypted data remains portable across TEE instances.
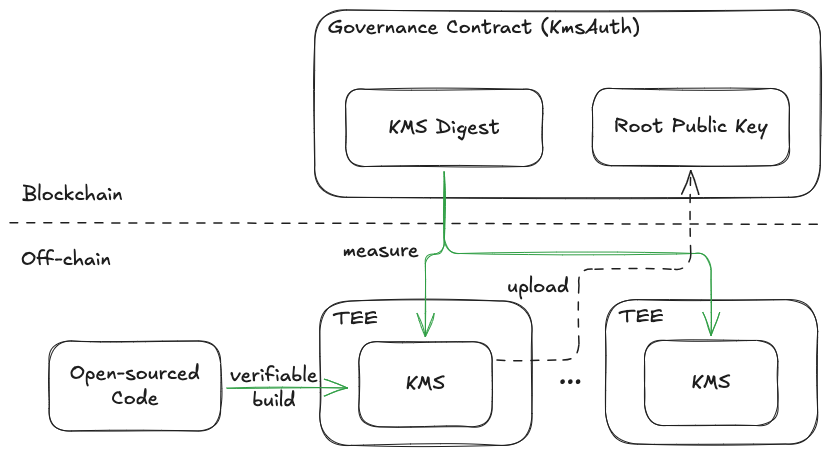
The architecture of dstack-kms combines on-chain governance through smart contracts with an off-chain P2P network of secret derivation service nodes. This design ensures both verifiability and resilience against compromise.
- The dstack-kms codebase is fully open-sourced, enabling thorough code and security reviews to verify key management logic and ensure the absence of backdoors.
- Executable binaries are produced with Github Actions, allowing verifiers to confirm that the
runtime code matches the reviewed source code. - The cryptographic digest of valid executables is published through the governance smart contract, creating an immutable reference for verification.
- Each service node operates within its own TEE instance. Critically, we rely on the TEE solely for measuring the executable and ensuring it matches the on-chain digest — not for the fundamental security of the key management process.
- Simple Duplication: The first node in the P2P network generates a cryptographically secure
random number as the root key, then shares it with other nodes after verifying their attestation reports. All nodes maintain identical copies of the root key and derive consistent encryption keys for applications. This approach maximizes availability — as long as at least one node remains operational, the root key can be recovered. - MPC-Based Key Generation: While simple duplication provides robust availability, it creates vulnerability to single-node compromises. Our MPC implementation uses Shamir’s Secret
Sharing scheme to distribute the root key across multiple nodes, ensuring that compromising
any individual node (or even up to t-1 nodes, where t is the configured threshold) does not
expose the root key. This approach also enables advanced features like key rotation without
requiring application reconfiguration.
- Application CA Key: Derived from the root CA key using the application’s unique identifier
registered on-chain. - Disk Encryption Key: Derived using a combination of the application identifier and instance
identifier, enabling secure storage with portability. - Environment Encryption Key: Derived using the application identifier alone, allowing secure
environment variable management across instances. - ECDSA Key: Derived from the root ECDSA key, providing applications with consistent cryptographic identity for signing operations.
contract, ensuring transparency and auditability. We discuss two distinct rotation mechanisms:
- Root Key Share Rotation: Our MPC-based implementation enables rotation of individual
key shares without modifying the root key itself. This process enhances root key security by
regularly updating the distribution mechanism while remaining transparent to applications, as
all derived application keys remain unchanged. - Root Key Rotation: In scenarios where the root key may have been compromised, we support
complete root key rotation. This process generates an entirely new root key and implements a
controlled handover period during which both old and new keys remain valid. This transition
window allows applications to re-encrypt their data with keys derived from the new root key
before the old root key is permanently destroyed, minimizing service disruption while enhancing security.
dstack-os: Hardware Abstraction Layer
dstack-os provides a comprehensive hardware abstraction layer with a minimized operating system image that bridges the gap between application containers and VM-level TEE implementations. This layer enables applications to deploy across diverse TEE environments without code modifications while maintaining security integrity. As a shared component across all TEE applications, dstack-os must be intrinsically secure and verifiable, with no administrative backdoors that could compromise program code or user data. VM-level TEE solutions typically require developers to provide complete system images encompassing bootloader, kernel, operating system, and application components. This requirement not only increases development complexity but also introduces potential security vulnerabilities through misconfigured system components. A secure and properly configured operating system environment fundamentally determines the security baseline for all TEE applications built upon it.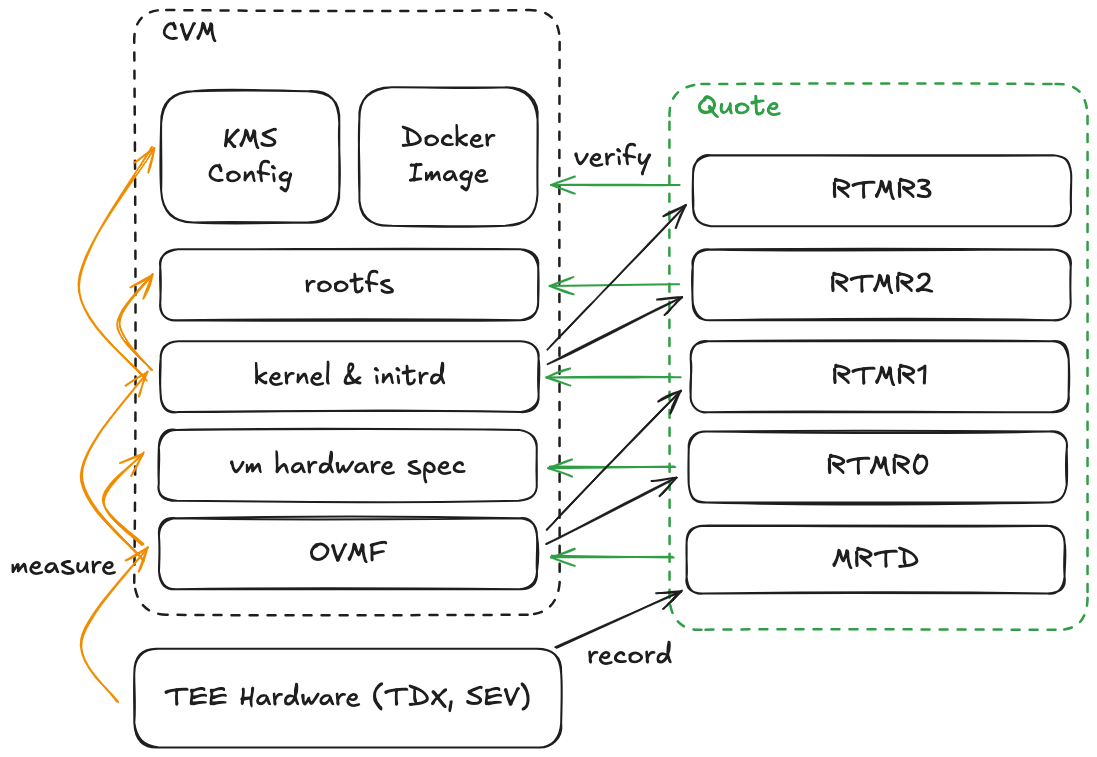
The architecture of dstack-os establishes a secure and verifiable startup chain from TEE hardware through to user applications.
order. During this process, each component measures the next one and records these measurements in hardware registers, which are ultimately incorporated into the TEE attestation report:
- Hypervisor: When application deployment initiates, the underlying hypervisor (the TDX module) loads the Open Virtual Machine Firmware (OVMF), enabling UEFI support for confidential virtual machines. The TDX module measures the OVMF code and records its cryptographic digest in the MRTD register, with the hypervisor’s integrity guaranteed by the TEE hardware
itself. - Open Virtual Machine Firmware (OVMF): The OVMF configures virtual machine hardware specifications (CPU, memory, and device configurations) and records the configuration measurement to the RTMR0 register. It then loads the Linux kernel and records the kernel
image measurement to the RTMR1 register. - Kernel: The kernel first loads an initial ramdisk (initrd) — a temporary in-memory filesystem
containing minimal command-line tools and disk encryption libraries. The initrd mounts the
root filesystem and then the kernel will call the OVMF to record a full measurement (including
kernel, initrd and RootFs to load) in the RTMR2 register. - Root Filesystem: The root filesystem (RootFs) is a read-only environment containing essential system libraries and tools. It manages the entire lifecycle of deployed applications, measuring application images along with their associated key management system and storing these measurements in the RTMR3 register. The RootFs serves two primary functions: (1) providing the runtime environment for user-level container images, and (2) managing application data encryption. It interfaces with dstack-kms to acquire encryption secrets and implements Linux Unified Key Setup (LUKS) to encrypt application data in isolated volumes. Its data integrity is ensured through dm-verity, a Merkle-tree-based block-level verification tool. Finally, the RootFs configures network ingress for the application and initiates execution.
builds, allowing anyone to review the code and generate identical artifacts for verification. This
approach provides significant benefits for applications requiring security reviews, as evaluators need only review the application code rather than the entire system image. Data Backup and Defense against Rollback Attacks A critical challenge in confidential computing is ensuring data durability and integrity, particularly against rollback attacks where adversaries attempt to revert applications to previous states to bypass security checks or reuse expired secrets. Our architecture provides comprehensive secure data backup support and implements robust anti-rollback mechanisms that application developers can integrate:
- Secure Backup: Application data is encrypted using keys derived from dstack-kms and can be backed up to external storage providers. Since encryption keys are not bound to specific TEE instances, data can be restored on any authorized TEE, supporting true portability and disaster recovery.
- Monotonic Counters: To prevent rollback attacks, developers can implement monotonic counters that increment with each critical data update, incorporating the counter value into the encrypted data. During restoration, applications verify that the counter value equals or exceeds the last known value, preventing replay of outdated snapshots.
Decentralized Code Management
A core principle of Zero Trust platforms is the enforcement of “Code is Law”, ensuring that application code operates as intended without unexpected modifications. While TEE hardware provides code integrity guarantees during execution, it cannot independently prevent administrators from deploying malicious code or making unauthorized modifications. Conversely, smart contracts have established robust methodologies for implementing programmable governance over code lifecycle management — such as multi-signature requirements that prevent single-actor manipulation. Our decentralized code management framework bridges these two worlds by placing TEE application governance under smart contract control, creating a transparent and auditable system for application deployment and updates that aligns with Web3 principles.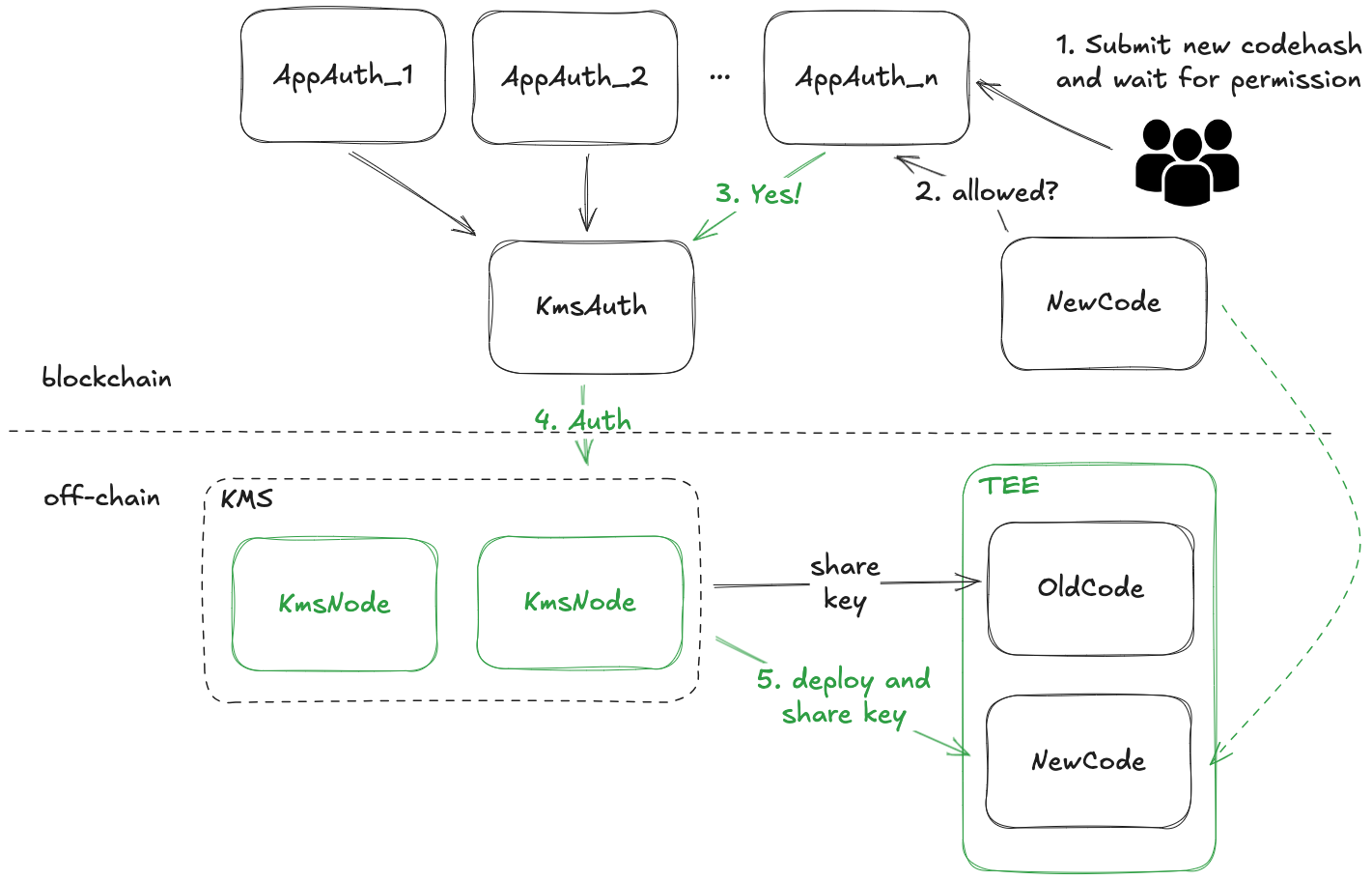
The architecture of decentralized code management integrates on-chain governance contracts with off-chain TEE through dstack-kms.
operation — from initial deployment to code updates — must first be initiated and authorized through the governance contracts before off-chain TEE instances can execute these operations. The governance framework implements a two-tier structure:
- KmsAuth Contract: Serves as the global authority controlling dstack-kms operations. This
contract maintains the registry of authorized dstack-os images, applications and their governance parameters, enforcing system-wide policies for TEE deployment. By controlling whether dstack-kms shares application secrets with specific TEE instances, the KmsAuth contract effectively determines whether applications can decrypt their data, thus controlling their complete lifecycle. - AppAuth Contracts: Individual governance contracts deployed for each application that define application-specific management rules. These contracts specify permissible code versions (through cryptographic hashes), authorized TEE instance identities, and upgrade approval requirements. This modular approach enables customized governance models ranging from traditional multi-signature schemes to complex DAO voting mechanisms, allowing each application to implement governance appropriate to its requirements.
secrets to TEE instances running code versions explicitly authorized by the governance contracts. This creates a cryptographically enforced governance system where unauthorized code versions cannot access application data, regardless of administrative privileges. To illustrate this mechanism, consider a code update process for an application using a multi-
signature AppAuth contract:
- Developers publish the new code version and submit its cryptographic hash to the AppAuth
contract. - The contract initiates the approval process, requiring signatures from designated key holders
(e.g., core developers, security auditors, and community representatives). - Each signature is recorded on-chain, creating an immutable audit trail of the approval process.
- Once the required signature threshold is reached, the AppAuth contract updates its registry of authorized code versions.
- The KmsAuth contract calls the corresponding AppAuth contract, and updates its authorization records accordingly.
- dstack-kms, which continuously synchronizes with the KmsAuth contract, begins providing application secrets to TEE instances running the newly approved code version.
- TEE instances can now deploy the new code with full access to encrypted application data.
of smart contracts, our decentralized code management framework ensures that applications truly embody the ”Code is Law” principle. Every aspect of the application lifecycle — from initial deployment to version updates and potential retirement — follows predefined, transparent rules that cannot be circumvented by any single entity, including the platform operators themselves.
Verifiable Domain Management
A complete Zero Trust platform must enable seamless verification for users across both Web3 and traditional Web2 environments. Our Verifiable Domain Management system completes the chain-of-trust by allowing standard Web browsers to cryptographically verify TEE applications without requiring any client-side modifications or specialized knowledge. This capability is critical for mainstream adoption, as it allows users to interact with confidentialapplications using familiar tools while maintaining the same security guarantees provided by the underlying TEE infrastructure. We implement this through two complementary components — dstack-ingress and dstack-gateway — both leveraging our novel Zero Trust TLS (ZT-TLS) protocol. The fundamental innovation in ZT-TLS is establishing cryptographic proof that a specific TLS
certificate (and therefore a domain) is exclusively controlled by a verified TEE application. This
creates a verification chain extending from the blockchain to standard HTTPS connections, enabling users to confirm application authenticity through familiar security indicators in their browsers.
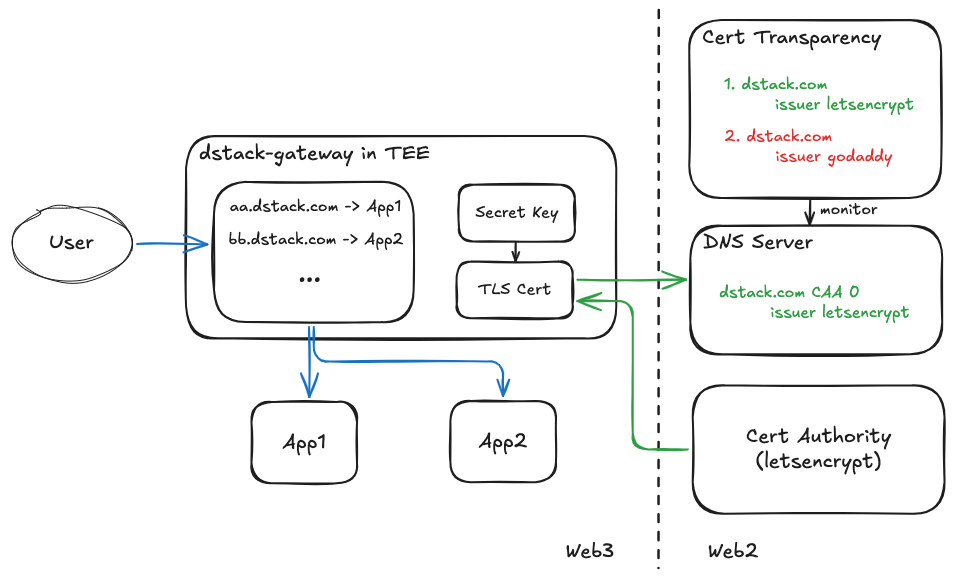
The Zero Trust TLS architecture establishes a cryptographically verifiable connection between standard web browsers and TEE applications through blockchain-anchored certificate management.
Zero Trust TLS Protocol
The ZT-TLS protocol addresses a critical challenge: how to cryptographically bind a domain to aspecific TEE application in a way that prevents unauthorized certificate issuance or domain hijacking. Our solution integrates three key components:
- TEE-Generated Certificates: The TEE application (specifically dstack-gateway) setups all
the information for the certificate, including Automated Certificate Management Environment
(ACME), the secret key and Certificate Signing Request (CSR), and request the CA (e.g. letsencrypt) to issue its TLS certificate using application secrets derived from dstack-kms. This ensures the private key never exists outside the TEE environment and creates a cryptographic link between the on-chain governance and the TLS certificate. - Certificate Authority Authorization (CAA): We leverage DNS CAA records to restrict
that only TEE-controlled ACME is valid, and which certificate authorities can issue certificates
for managed domains. By configuring CAA records to only authorize certificates from specific
issuers (which verify TEE attestation), we prevent unauthorized certificate issuance through
alternative validation methods. - Certificate Transparency (CT) Monitoring: To protect against unauthorized DNS record
modifications, we implement continuous monitoring of Certificate Transparency logs. This allows detection of any unauthorized certificates and provides an immutable audit trail of certificate issuance history. It is worth noting that such monitoring service can be implemented by anyone to be truly decentralized.
Implementation Components
We provide two complementary implementations to accommodate different application requirements:- dstack-gateway: A fully managed reverse proxy running within a TEE that provides immediate domain verification with zero application code changes. Applications register with dstack-gateway through a simple API call, during which dstack-gateway verifies the application’s remote attestation report. Once verified, applications receive a subdomain under a pre-registered wildcard domain (e.g., app-id.dstack.com), with all TLS termination and certificate management handled automatically.
- dstack-ingress: A more flexible solution for applications requiring custom domain names.
dstack-ingress provides libraries and services that enable applications to manage their own TLS certificates while maintaining the same verification guarantees. This approach requires minimal integration work while supporting application-specific domain requirements. When the customized domains are enabled, our gateway will fallback to TLS passthrough mode, where the TLS connection is directly established between the client and the application.
Security Guarantees and Protections
Our Verifiable Domain Management system provides several critical security guarantees:- Certificate Provenance Verification: Users can verify that the TLS certificate presented by
an application was issued to a legitimate TEE environment with the ZT-TLS protocol above. - Domain Binding Integrity: The combination of CAA records and Certificate Transparency
monitoring ensures that domains remain bound to their designated TEE applications, preventing unauthorized certificate issuance. - Tamper-Evident Certificate Changes: Any unauthorized attempts to modify domain configurations or issue alternative certificates are detected through Certificate Transparency monitoring, with alerts propagated to clients.

